题目描述:给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
方法一:迭代
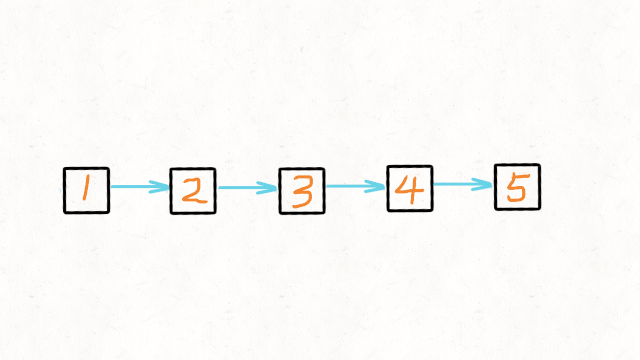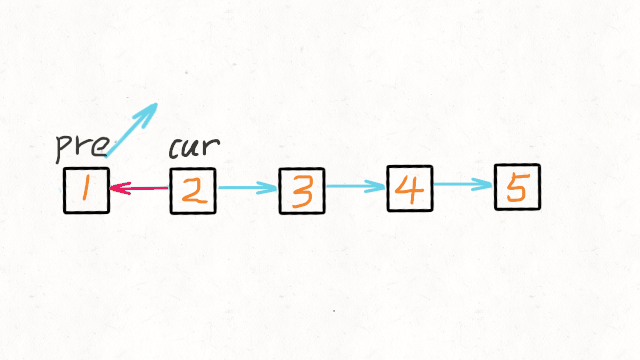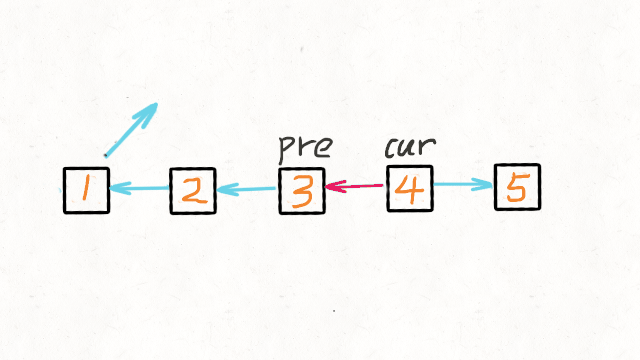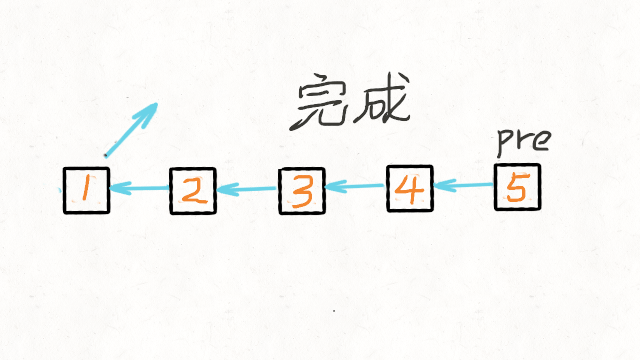
1 | /** |
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。需要遍历链表一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
执行结果:通过
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:38.1 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了70.48%的用户
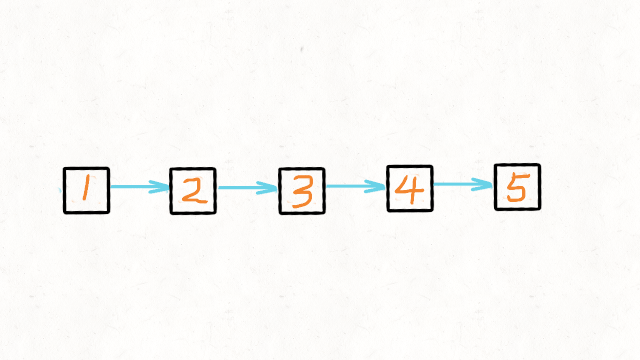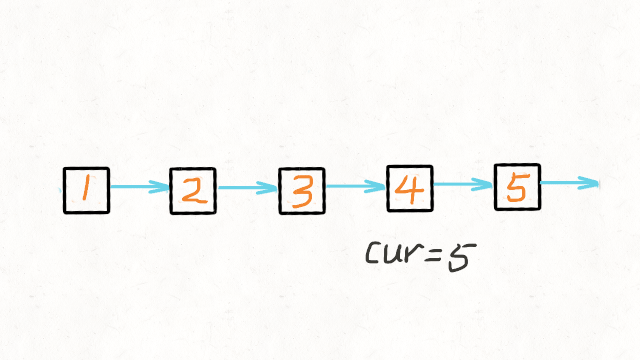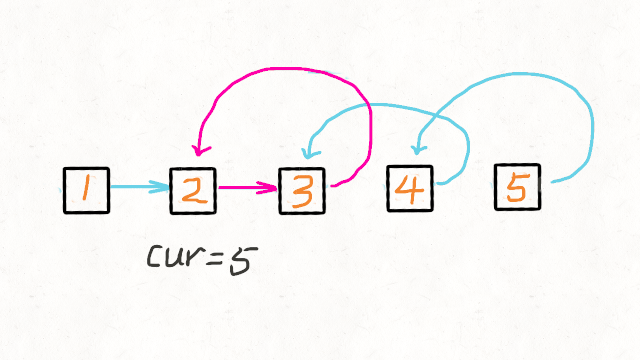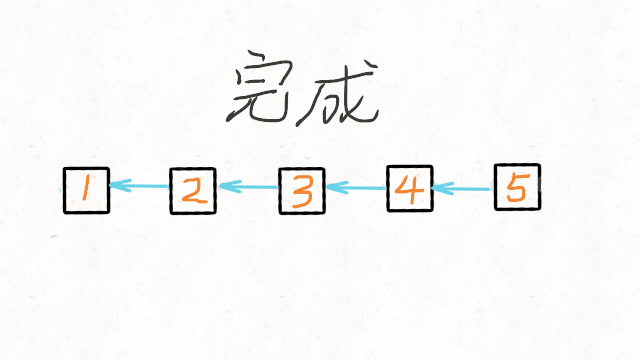
方法二:递归
1 | class Solution { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。需要对链表的每个节点进行反转操作。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是链表的长度。空间复杂度主要取决于递归调用的栈空间,最多为 n 层。
执行结果:通过
执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
内存消耗:38.5 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了8.90%的用户

